I have been working on studies explicating the Network Agenda Setting Model (NAS), the third level of agenda setting theory, since 2011. The NAS model asserts that
the salience of the network relationships among objects and/or attributes, in addition to discrete individual elements, can be transferred from the news media to the public’s mind.
Here is a graph that shows the difference between the traditional approach of agenda setting theory and the Network Agenda Setting Model.
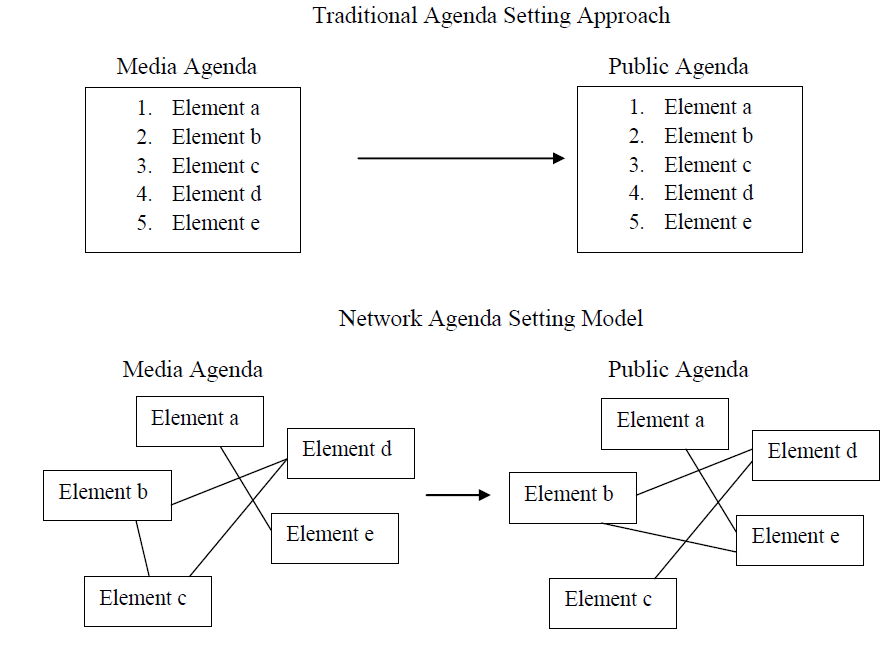
The empirical studies I have conducted with colleagues found that media agenda networks were significantly correlated with the public agenda networks in various socio-cultural contexts. The NAS model can also be used to examine agenda building, intermedia agenda setting and other media effects.
Selected NAS publications:
The first two conference papers:
- Guo, L. & McCombs, M. (2011). Network agenda setting: A third level of media effects. Paper presented at the ICA annual conference, Boston, May 2011.
- Guo, L. & McCombs, M. (2011). Toward the third level of agenda setting theory: A Network Agenda Setting Model. Paper presented at the AEJMC annual conference, St. Louis, August 2011.
Book:
- Guo, L. & McCombs, M. (Eds.) (2016). The power of information networks: New directions for agenda setting. New York: Routledge.
Peer-reviewed journals:
- Guo, L. (2012). The Application of Social Network Analysis in Agenda Setting Research: A Methodological Exploration. Journal of Broadcasting & Electronic Media, 56(4), 616-631.
- Vargo, C., Guo, L., Shaw, D., & McCombs, M. (2014). Network issue agendas on Twitter during the 2012 U.S. presidential election. Journal of Communication, 64(2),296-316.
- Vu, H. T., Guo, L., & McCombs, M. (2014). Exploring “the world outside and the pictures in our heads”: A network agenda setting study. Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly, 91(4), 669-686.
- Guo, L., et al. (2015). Coverage of the Iraq War in the United States, Mainland China, Taiwan and Poland. A transnational network agenda-setting study. Journalism Studies, 16 (3), 343-362.
- Guo, L. & Vargo, C. (2015). The power of message networks: A big-data analysis of the Network Agenda Setting Model and issue ownership. Mass Communication & Society, 18(5), 557-576.
- Vargo, C. & Guo, L. (2016). Networks, big data, and intermedia agenda-setting: an analysis of traditional, partisan, and emerging online U.S. news. Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly.
- Guo, L., Mays, K., & Wang, J. (2019). Whose Story Wins on Twitter? Visualizing the South China Sea dispute. Journalism Studies, 20(4), 563-584.
- Chen, H., Guo, L., & Su, C. (2020). Network Agenda Setting, Partisan selective exposure, and opinion repertoire: The effects of pro- and counter-attitudinal media in Hong Kong. Journal of Communication, 70(1), 35-59.